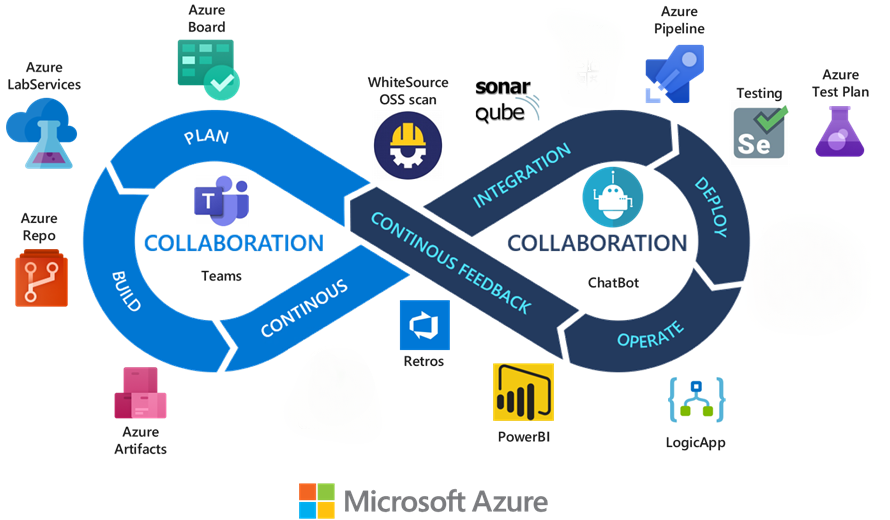
Azure DevOps is a cloud-based platform that provides integrated tools for software development teams. It includes everything you need to plan work, collaborate on code, build applications, test functionality, and deploy to production.
Azure DevOps offers a spectrum of service models to accommodate the unique needs of every team. The free access version helps small teams get started quickly, while the versatile subscription and pay-per-use plans support comprehensive project management.
Key characteristics:
- End-to-end project management: Azure DevOps stands as a cohesive suite of services designed to support the complete lifecycle of your software projects. It encompasses everything from initial planning and development, through rigorous testing, to final deployment.
- Client/server model delivery: Azure DevOps operates on a client/server model, offering flexibility in how you interact with its services. The web interface provides a convenient way to utilize most services and is compatible with all major browsers. Additionally, certain services like source control, build pipelines, and work tracking offer client-based management options for enhanced control.
- Flexible and scalable service options: Azure DevOps caters to teams of all sizes by offering a range of service options. For small teams, many services are complimentary, ensuring that you have access to robust project management tools without any initial investment. For larger teams or more advanced needs, services are accessible through a subscription model or on a pay-per-use basis.
Core services
Azure DevOps includes the following integrated services:

Azure Boards: Plan and track work using Agile tools, Kanban boards, backlogs, and dashboards. Create work items like user stories, bugs, and tasks. Use sprint planning, burndown charts, and velocity tracking. Customize workflows and work item types to match your team’s process.
Example scenario: A product team planning a mobile app feature creates user stories for “user sign-in,” tracks bugs found during development, and uses sprint boards to monitor progress during two-week iterations.
Azure Repos: Host unlimited private Git repositories or use Team Foundation Version Control (TFVC) for source code management. Features include branch policies, pull requests with code reviews, conflict resolution, and integration with popular IDEs and editors.
Example scenario: Development team members create feature branches for new functionality, submit pull requests for code review, and use branch policies to ensure all code is reviewed and tested before merging to the main branch.
Azure Pipelines: Build, test, and deploy applications with CI/CD pipelines that work with any language, platform, and cloud. Supports Docker containers, Kubernetes, and deployments to Azure, AWS, Google Cloud, or on-premises. Includes parallel jobs, deployment gates, and release approvals.
Example scenario: Every code commit triggers an automated pipeline that builds a .NET web application, runs unit tests, creates a Docker container, and deploys to staging environment for testing before production release.
Azure Test Plans: Plan, execute, and track testing with manual test cases, exploratory testing sessions, and automated test integration. Create test suites, track test results, capture screenshots and videos, and generate detailed test reports.
Example scenario: QA team creates test cases for user registration flow, executes manual tests on different browsers, captures screenshots of issues, and links test results to user stories for traceability.
Azure Artifacts: Create, host, and share packages like NuGet, npm, Maven, Python, and Universal packages with your team and organization. Integrate with build pipelines, manage package versions, and control access with upstream sources and retention policies.
Example scenario: Development team creates a shared authentication library, publishes it as a NuGet package to Azure Artifacts, and references it across multiple projects while controlling access to internal packages.
How Azure DevOps services work together
The following diagram shows how the services integrate throughout the development lifecycle:
┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ Azure Boards │ │ Azure Repos │ │ Azure Pipelines │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ • Plan features │────│ • Store code │────│ • Build apps │
│ • Track bugs │ │ • Code reviews │ │ • Run tests │
│ • Manage sprints│ │ • Branch policies│ │ • Deploy code │
└─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘
│ │ │
│ │ │
▼ ▼ ▼
┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ Azure Test Plans│ │ Azure Artifacts │ │ Dashboards │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ • Test planning │ │ • Package feeds │ │ • Project views │
│ • Manual testing│◄───│ • Version control│───►│ • Team metrics │
│ • Test reporting│ │ • Dependency mgmt│ │ • Build status │
└─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘
Flow: Plan → Code → Build → Test → Deploy → Monitor → Repeat
Typical workflow:
- Plan work items in Azure Boards
- Code features in Azure Repos with pull requests
- Build and package with Azure Pipelines and Azure Artifacts
- Test manually and automatically using Azure Test Plans
- Deploy through Azure Pipelines to various environments
- Monitor progress and metrics via Dashboards
- Iterate based on feedback and new requirements
For more information, see Tools and clients that connect to Azure DevOps.